Cephalic Region: The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Your Head’s Vital Zone
Let’s talk about something that sits right at the top of your game—your cephalic region! Yeah, we’re diving deep into the world of your head, its anatomy, function, and why it matters more than you might think. Whether you’re a science enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or just someone curious about what makes our bodies tick, this article’s got you covered. So buckle up, because we’re about to explore the epicenter of your body’s control panel.
The cephalic region, or simply put, your head, is not just a place where your brain resides. It’s a powerhouse packed with sensory organs, muscles, bones, and tissues that work together like a well-oiled machine. But what exactly is the cephalic region, and why should you care? Well, for starters, it’s the command center of everything you do—from thinking to breathing, seeing, hearing, and even tasting. And trust me, understanding it better could change the way you approach your health.
Here’s the deal: knowledge is power. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid grasp of the cephalic region, its structure, and how it impacts your daily life. Plus, we’ll throw in some fun facts, expert insights, and actionable tips to keep your head in top shape. Ready? Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- What is the Cephalic Region?
- Anatomy of the Cephalic Region
- Key Functions of the Cephalic Region
- Common Issues Affecting the Cephalic Region
- Health Tips for the Cephalic Region
- Biological Significance of the Cephalic Region
- Evolutionary Perspective on the Cephalic Region
- Medical Advancements in Cephalic Health
- Busting Myths About the Cephalic Region
- Wrapping Up: Why the Cephalic Region Matters
What is the Cephalic Region?
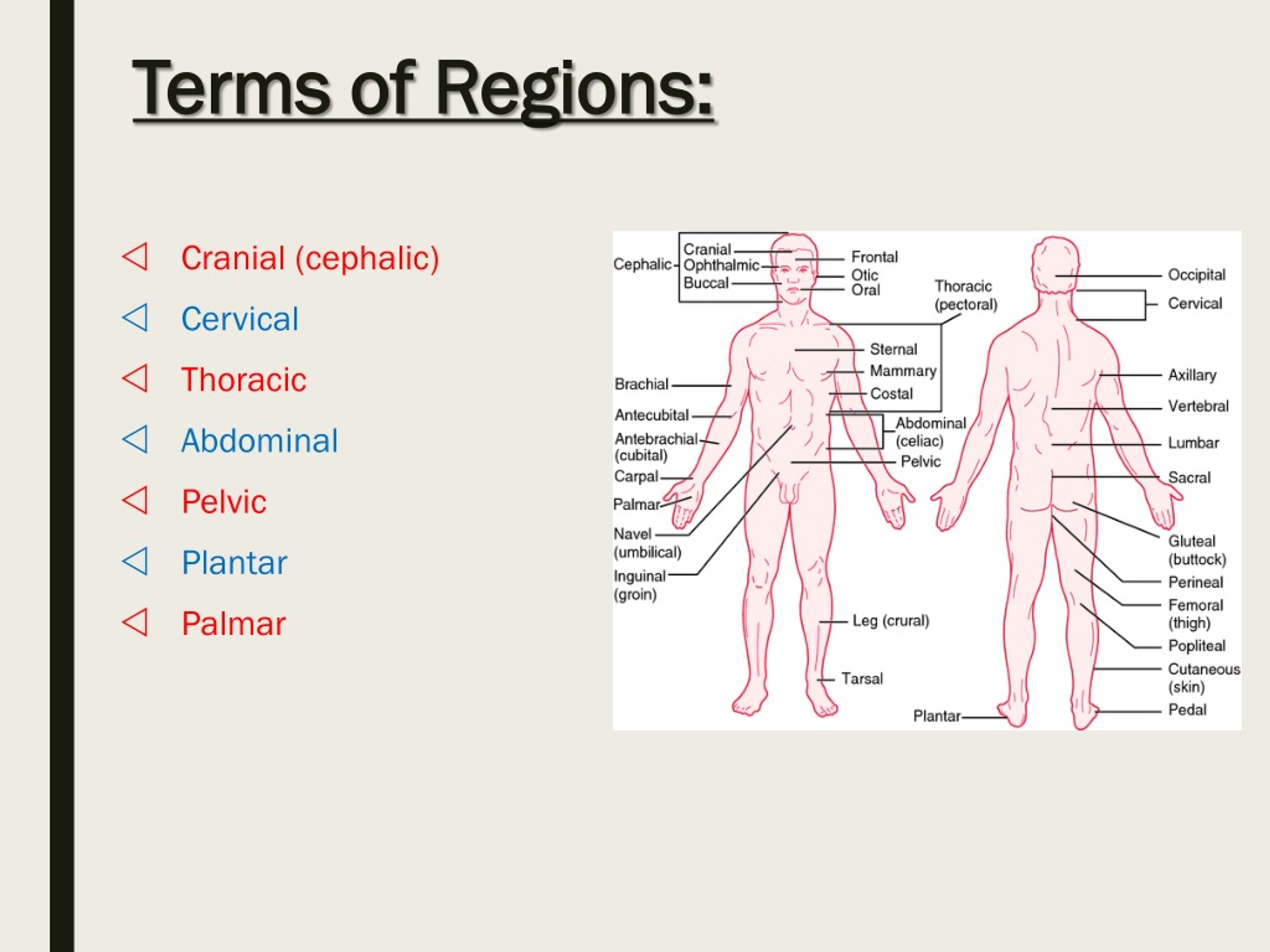
The cephalic region refers to the anatomical area that makes up your head. It’s the part of your body that houses your brain, sensory organs, and various other structures that allow you to interact with the world around you. Think of it as the cockpit of your body—where all the critical systems are managed and controlled.
But here’s the kicker: the cephalic region isn’t just about what’s inside. It also includes the external features like your face, skull, and even your hair. All these components work together to ensure that you can think clearly, move smoothly, and stay connected to your environment. And if you’re wondering why this matters so much, just consider this—your head is the first thing people see when they look at you. So yeah, it’s kind of a big deal!
Why is the Cephalic Region Important?
Let’s break it down. The cephalic region is home to some of the most vital organs in your body:
- Brain: The control center for all your thoughts, emotions, and actions.
- Eyes: Your windows to the world, allowing you to see and interpret visual information.
- Ears: Responsible for hearing and maintaining balance.
- Nose: Not just for smelling, but also for filtering air as it enters your body.
- Mouth: Used for eating, speaking, and expressing emotions.
Without a properly functioning cephalic region, life as we know it would be pretty tough. So, it’s safe to say that taking care of this area is essential for overall well-being.
Anatomy of the Cephalic Region
Now, let’s dive deeper into the anatomy of the cephalic region. What’s really going on under the surface? Well, it’s a complex network of bones, muscles, nerves, and soft tissues that work together seamlessly. Here’s a quick rundown:
Bones
The skull forms the protective casing around your brain and other structures. It consists of several bones, including:
- Frontal Bone: Forms the forehead and upper part of the eye sockets.
- Parietal Bones: Located on either side of the skull, forming the sides and top.
- Temporal Bones: Found near the ears, housing structures like the auditory canal.
- Occipital Bone: Forms the back and base of the skull.
Muscles
Muscles in the cephalic region help you move your face, chew food, and even speak. Some key players include:
- Masseter: A powerful muscle used for chewing.
- Orbicularis Oculi: Controls movements around the eyes.
- Facial Muscles: Allow you to express emotions through facial expressions.
Nerves
Without nerves, your cephalic region wouldn’t be able to function properly. The cranial nerves are responsible for transmitting signals between your brain and the rest of your body. Some important ones include:
- Optic Nerve: Carries visual information from the eyes to the brain.
- Vestibulocochlear Nerve: Controls hearing and balance.
- Trigeminal Nerve: Provides sensation to the face and controls chewing muscles.
Key Functions of the Cephalic Region
So, what does the cephalic region actually do? Here are some of its main functions:
- Thinking and Processing: The brain is responsible for all cognitive processes, including memory, reasoning, and decision-making.
- Sensory Perception: Your eyes, ears, nose, and mouth gather information from the environment and send it to your brain for processing.
- Movement Control: The cephalic region helps coordinate voluntary and involuntary movements, ensuring smooth functioning of the body.
- Emotional Expression: Facial muscles allow you to convey emotions through expressions, making communication more effective.
It’s fascinating how all these functions come together to create the amazing machine that is your head. And if you think about it, every single thing you do involves the cephalic region in some way or another.
Common Issues Affecting the Cephalic Region
Unfortunately, the cephalic region isn’t immune to problems. Here are some common issues that can affect this vital area:
- Headaches: One of the most prevalent complaints, headaches can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain.
- Migraines: A more severe form of headache, often accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light.
- Concussions: Traumatic brain injuries that can occur due to a blow to the head.
- Ear Infections: Inflammation of the ear canals, leading to pain and hearing difficulties.
If you’re experiencing any of these issues, it’s important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
Health Tips for the Cephalic Region
Want to keep your cephalic region in tip-top shape? Here are some practical tips:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain optimal brain function and prevents headaches.
- Protect Your Head: Wear helmets during activities like cycling or skiing to reduce the risk of injury.
- Practice Good Posture: Keeping your head and neck aligned can prevent strain and discomfort.
- Get Enough Sleep: Rest is crucial for brain health and overall well-being.
These simple steps can go a long way in ensuring that your cephalic region remains healthy and functional.
Biological Significance of the Cephalic Region
From an evolutionary standpoint, the cephalic region plays a crucial role in survival. It allows us to perceive our surroundings, make decisions, and respond to threats. Without it, we wouldn’t be able to adapt to changing environments or communicate effectively with others.
Moreover, the cephalic region is what sets humans apart from other species. Our advanced brains and sensory capabilities enable us to create art, solve complex problems, and build civilizations. It’s truly the epicenter of human achievement.
Evolutionary Perspective on the Cephalic Region
Over millions of years, the cephalic region has evolved to become the sophisticated system we know today. Early ancestors relied heavily on their senses to survive, and as time went on, the brain grew larger and more complex. This allowed for the development of language, culture, and technology.
But evolution isn’t just about physical changes. It’s also about how we use our cephalic region to interact with the world. Today, we rely on our heads for everything from operating smartphones to solving global challenges. And as we continue to evolve, who knows what new capabilities we’ll unlock?
Medical Advancements in Cephalic Health
Thanks to modern medicine, we now have a better understanding of the cephalic region and how to treat its ailments. Techniques like MRI scans and CT imaging allow doctors to visualize the brain and other structures in unprecedented detail. Additionally, advancements in neurosurgery and pharmacology have improved outcomes for patients with cephalic-related conditions.
Looking ahead, researchers are exploring innovative treatments like stem cell therapy and gene editing to address complex issues affecting the cephalic region. These breakthroughs could revolutionize the way we approach health and wellness in the future.
Busting Myths About the Cephalic Region
There’s a lot of misinformation out there when it comes to the cephalic region. Let’s clear up some common myths:
- Myth: You only use 10% of your brain. False! Studies show that we use virtually every part of the brain, even if not all at the same time.
- Myth: Hair grows faster when shaved. Nope! Shaving doesn’t affect hair growth rate or thickness.
- Myth: Cracking your neck is harmful. While it may cause discomfort, occasional cracking isn’t harmful unless done excessively or incorrectly.
By separating fact from fiction, we can make more informed decisions about our health and well-being.
Wrapping Up: Why the Cephalic Region Matters
And there you have it—a comprehensive look at the cephalic region and why it’s so important. From its anatomy and functions to common issues and health tips, we’ve covered a lot of ground. But the bottom line is this: your head is an incredible machine that deserves care and attention.
So, take a moment to appreciate the amazing things your cephalic region does for you every day. And remember, if you ever feel something’s off, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Your head deserves the best!
Got any thoughts or questions? Drop a comment below, and let’s keep the conversation going. And while you’re at it, why not check out some of our other articles for more insightful reads?
Cephalic Region Mastering Head And Brain Anatomy Dulab Innovations

Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology CHAPTER 7 Anatomy of Bones
PPT Introduction to Anatomy Anatomical Terms & Skeletal System